I spend a lot of time writing about the good stuff, like sex on traditional Philippine furniture. (For example, here and here.) But my blog is not all fun and games. I have set my novels in the Philippine-American War, and that was a horrible war. I have posted before on how the war began, how it was conducted, and a little bit about battles and operations—but I have avoided this particular post for a long time. This is the post on the water cure.
If you’re not feeling like anything disturbing, heavy, or possibly enraging, do go check out those other posts about sexy times on antique furniture. Come back to this another time.
Warning: If you do choose to stay, please note that this post discusses a practice at least partly motivated by racism. A few of the historic sources include racist language or judgments.
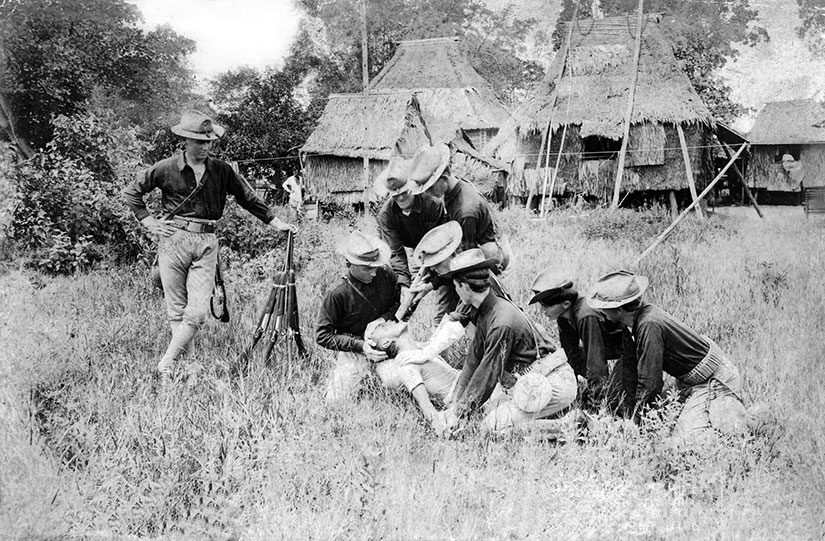

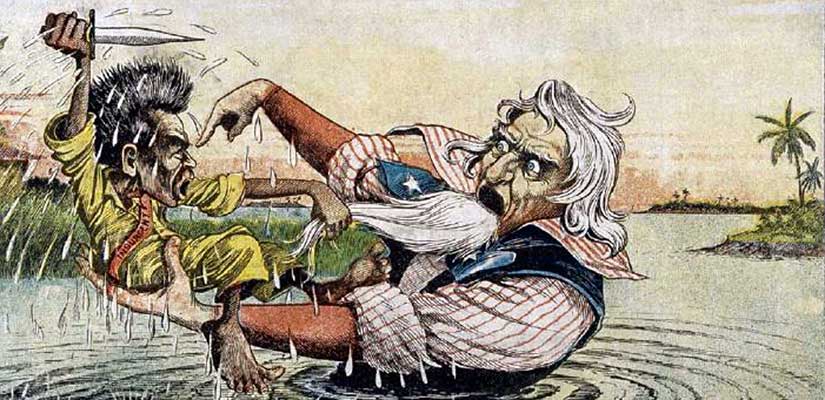
The water cure is a little different than modern-day waterboarding. In waterboarding, water is poured over a cloth covering the face to simulate the sensation of drowning. That may seem like it’s some sort of fake out, but it does cause real injuries. The water cure, though, is even more physical. In this practice, they laid a prisoner on his back, stood another man on each hand and foot, and forced a hollow tube into the victim’s throat. Through the tube they poured an entire pail of saltwater, dished up with a little sand to inflict a more severe punishment. When the prisoner did not give up, they poured in another pailful. Once the unlucky victim’s belly was “distended to the point of bursting,” a soldier would “tap” it with the butt of his gun. If the water did not spout high enough, they would jump up and down on his stomach. In the words of A. F. Miller of the 32nd Volunteer Infantry Regiment: “They swell[ed] up like toads. I’ll tell you it [was] a terrible torture.”
According to historian Darius Rejali, “Even a small amount of water in the glottis causes violent coughing, initiating a fight-or-flight response…triggering desperate efforts to break free. The supply of oxygen…is exhausted within seconds. While this is sometimes called ‘an illusion of drowning,’ the reality is that death will follow if the procedure is not stopped in time.” And it did.
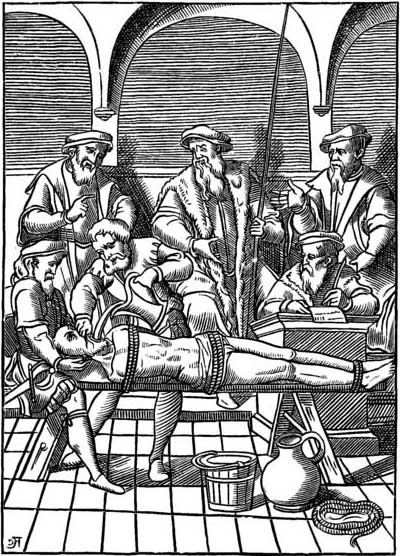
This cruel technique was first introduced in the Spanish Inquisition and then spread throughout medieval Europe. The Spanish brought it to the Philippines, trained local scouts in the practice, and then those scouts taught the American soldiers. Some soldiers were more eager than others to use it. Major Edwin Glenn and “Glenn’s Brigade” were infamous for water curing thirteen priests of Samar—half of the clergy on the island—and they even killed one of the priests in the process. This was a part of the “howling wilderness” period.
When the American public found out about what Glenn had been up to in the islands, he was court-martialed. Actually, Glenn was brought to court three times. The first time he was found guilty of uncivilized conduct in war, despite his claims that the water cure could be a remedy for dengue fever. (Yes, he really did try that excuse. He even called witnesses to testify to this. It’s in the 1902 archives of the Manila Times.) He was given a one-month suspension and fined fifty dollars. (In comparison, the man he water-cured that time, the mayor of Igbaras in Iloilo, was sentenced to ten years hard labor for what he was confessed under duress.) Glenn was court-martialed a second time for killing seven prisoners of war, though he was acquitted. Finally, he was sued in civil court for $15,000 (over $420,000 in 2016 dollars) by a former revolutionary named Calda. I have never found out how this last case ended, but I do appreciate the hutzpah that encouraged it. Since Glenn retired as a brigadier general from the Army, I can assume that nothing stuck.
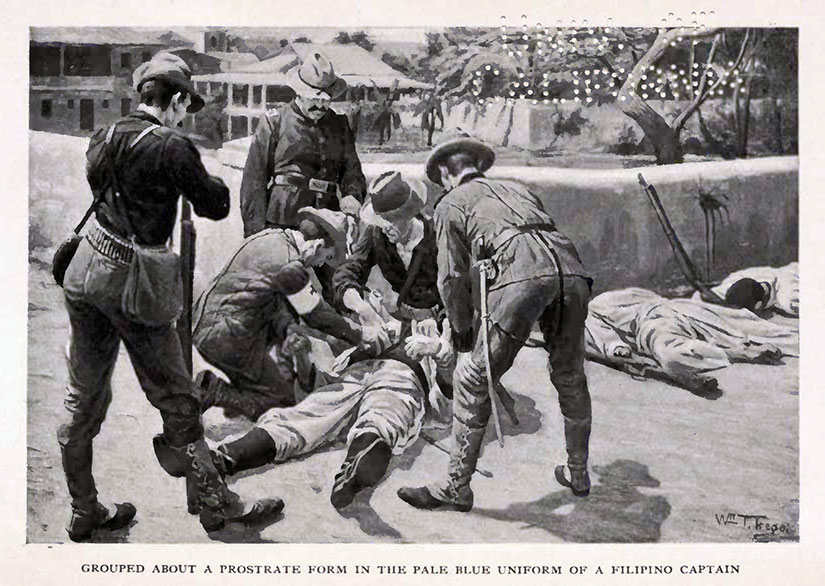

Stories like the ones about Glenn’s Brigade were said to have “covered with a foul blot the flag which we all love and honor” by Senator Hoar (R) of Massachusetts. This led to an official inquiry in the Senate by the Committee on the Philippines. The discussion was fractious. Henry Cabot Lodge, another Republican senator from Massachusetts, chaired the committee—not because he wanted to uncover atrocities, but because he wanted to steer the committee away from doing any such thing. (Yes, two senators from the same state and the same party were sworn enemies on this issue.)
Lodge, in particular, did not want to criticize anything that soldiers did in the name of empire. He said that the water cure had:
…grown out of the conditions of warfare, of the war that was waged by the Filipinos themselves, a semicivilized people, with all the tendencies and characteristics of Asiatics, with the Asiatic indifference to life, with the Asiatic treachery and the Asiatic cruelty, all tinctured and increased by three hundred years of subjection to Spain.
Way to pass the buck, dude. (I’d like to remind readers that the water cure originated in Europe, not Asia.)

Despite Senator Lodge’s and Senator’s Beveridge’s (R-IN) staunch support of “military necessity,” soldiers did testify to atrocities they witnessed in the Philippines. Even Lt. General Nelson A. Miles told the Secretary of War that the conflict had been fought with “marked severity.” The evidence, and Miles’s remarks, were printed in the newspapers across the United States.
Novelist and prominent anti-imperialist Mark Twain wrote about the hypocrisy of Americans fighting a war to “civilize” another country and then succumbing to the very barbarism they sought to expunge. His essay “To the Person Sitting in Darkness” is one of his best and most biting pieces of satire:
The Person Sitting in Darkness is almost sure to say: “There is something curious about this — curious and unaccountable. There must be two Americas: one that sets the captive free, and one that takes a once-captive’s new freedom away from him, and picks a quarrel with him with nothing to found it on; then kills him to get his land.” …And as for a flag for the Philippine Province, it is easily managed. We can have a special one — our States do it: we can have just our usual flag, with the white stripes painted black and the stars replaced by the skull and cross-bones.

In the midst of the 1902 crisis, President Theodore Roosevelt tried to limit the damage to blaming a few weak men:
The temptation to retaliate for the fearful cruelties of a savage foe is very great, and now and then it has been yielded to. There have been a few, and only a few, such instances in the Philippines, and punishment has been meted out with unflinching justice to the offenders.
But was this truly just a few bad apples? Certainly, many of the soldiers knew of the practice. They even sang songs to it.

The commanders in the field knew better than to underestimate the problem. In 1903, an expedition in Surigao declared:
…let there be no water curing or severity that is not plainly authorized without straining interpretations of [the] law of war… .Anyone who disgraces our uniform by engaging in such barbarous practices will be punished on the spot… .Success will not be marred by any well founded complaints of undue severity and flagrant misconduct.
What does this prove? That seventy years before Vietnam and one hundred years before Iraq, there was a national conversation about how America should exercise its authority abroad. Unfortunately, though, nothing was concluded. The controversy was quelled by a conveniently timed declaration of “peace” in the islands on July 4, 1902. (It was not peace, though: fighting would continue until 1913, including other, bigger atrocities, like the hundreds of civilian dead at Bud Dajo.)
When the military handed power over to a civil government under Governor William Howard Taft, Americans at home believed their problems were solved. However, because America did not finish the conversation, the public was forced to have it all over again in 1969 (when the My Lai massacre story broke) and in 2004 (when the Abu Ghraib torture and prisoner abuse scandal broke). Does the end always justify the means? What if the means makes the end goal—peace—impossible? Unfortunately, Americans may be tiring of these questions before they can come to a consensus about the answers.
The administration of President Donald J. Trump has recently declared its intention to hide a 2014 report describing the CIA’s harsh detention and interrogation programs. By returning the document to Congress, this shields the report from ever being accessible to the American public through the Freedom of Information Act. Throwing this 6700-page report down the memory hole has more of a precedent than we would like to think. We’ve forgotten before.





 These days, the houses of Newport’s Cliff Walk and Bellevue Avenue are open to the public. Crowds mill through
These days, the houses of Newport’s Cliff Walk and Bellevue Avenue are open to the public. Crowds mill through 




